Research
[Clinical Infectious Diseases] Consistent Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Saliva

Clinical Infectious Diseases ,12 February 2020
Kelvin Kai-Wang To, Owen Tak-Yin Tsang, Cyril Chik-Yan Yip, Kwok-Hung Chan, Tak-Chiu Wu, Jacky Man-Chun Chan, Wai-Shing Leung, Thomas Shiu-Hong Chik, Chris Yau-Chung Choi, Darshana H Kandamby, David Christopher Lung, Anthony Raymond Tam, Rosana Wing-Shan Poon, Agnes Yim-Fong Fung, Ivan Fan-Ngai Hung, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, Jasper Fuk-Woo Chan, Kwok-Yung Yuen
Highlights:
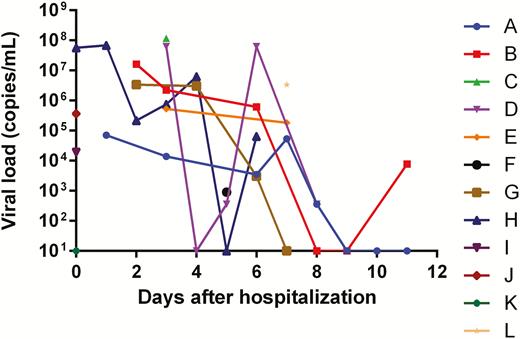
- A total of 12 patients with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in Hong Kong were included in this study. SARS-CoV-2 could be detected in the saliva specimens of 11 of the 12 (91.7%) patients studied.
- Serial saliva specimens showed gradual declines in salivary SARS-CoV-2 RNA loads in these patients.
- Live virus was detected in saliva by viral culture.
- Advantages in using saliva specimens for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2:
– Saliva specimens can be provided by the patient easily without any invasive procedures to reduce the risk of nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
– Allows specimen collection outside the hospitals where airborne-infection isolation rooms are not available, such as in outpatient clinics or in the community.
– Use of saliva specimens will eliminate the waiting time for specimen collection - Our results have demonstrated the potential for saliva to be a non-invasive specimen type for the diagnosis and viral load monitoring of SARS-CoV-2.

![Photo of [Nature Microbiology] Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/Image-2-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of [Cell Reports Medicine] Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in golden Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/fx1_lrg-e1601870075235-390x220.jpg)