Research
[Journal of Clinical Microbiology] Improved molecular diagnosis of COVID-19 by the novel, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay validated in vitro and with clinical specimens
Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 4 March 2020
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
Highlights:
- Highly sensitive and specific laboratory diagnostics are important for controlling the rapidly evolving SARS-CoV-2-associated Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic.
- In this study, we developed and compared the performance of three novel real-time RT-PCR assays targeting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)/helicase (Hel), spike (S), and nucleocapsid (N) genes of SARS-CoV-2 with that of the reported RdRp-P2 assay which is used in >30 European laboratories.
- Among the three novel assays, the COVID-19-RdRp/Hel assay had the lowest limit of detection in vitro (1.8 TCID50/ml with genomic RNA and 11.2 RNA copies/reaction with in vitro RNA transcripts).
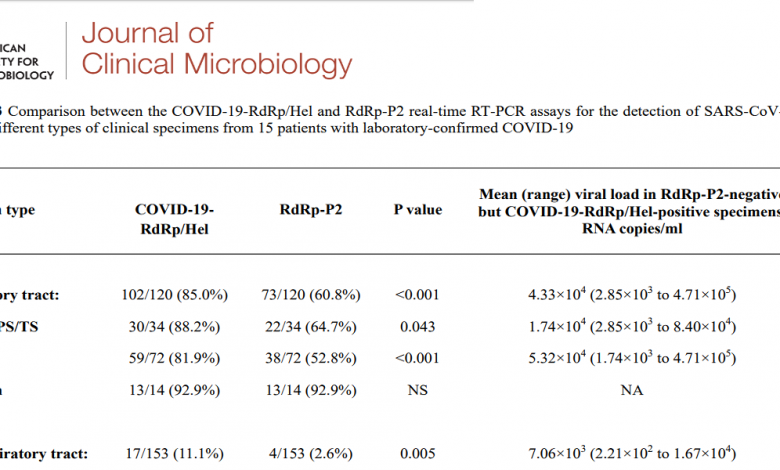
- Among 273 specimens from 15 patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in Hong Kong, 77 (28.2%) were positive by both the COVID-19-RdRp/Hel and RdRp-P2 assays. The COVID-19-RdRp/Hel assay was positive for an additional 42 RdRd-P2-negative specimens [119/273 (43.6%) vs 77/273 (28.2%), P<0.001], including 29/120 (24.2%) respiratory tract specimens and 13/153 (8.5%) non-respiratory tract specimens.
- The mean viral load of these specimens was 3.21×104 RNA copies/ml (range, 2.21×102 to 4.71×105 RNA copies/ml).
- The highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel assay may help to improve the laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19.

![Photo of [Nature Microbiology] Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/Image-2-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of [Cell Reports Medicine] Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in golden Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/fx1_lrg-e1601870075235-390x220.jpg)