Research
[Lancet] Nowcasting and forecasting potential domestic and international spread of COVID-2019: a modelling study
The Lancet, 31 January 2020
Prof Joseph T Wu, Kathy Leung, Prof Gabriel M Leung
Highlights
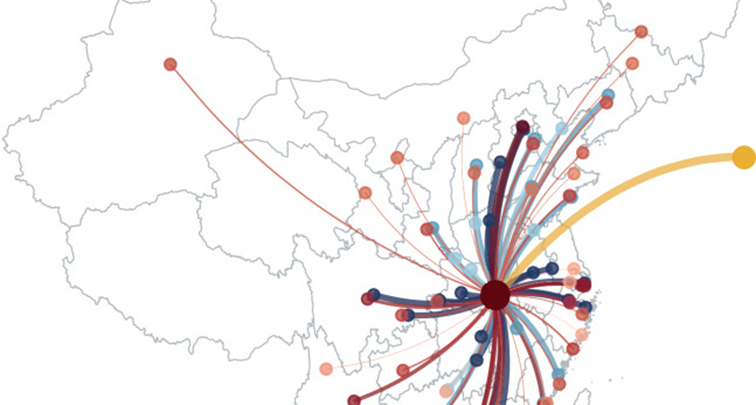
- New modeling research estimates up to 75,800 individuals in the Chinese city of Wuhan may have been infected with the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) as of January 25, 2020.
- Not everyone infected would require or seek medical attention. During the urgent demands of a rapidly expanding epidemic of a completely new virus, some of those infected may be undercounted in the official register.
- The apparent discrepancy between the modeled estimates of infections and the actual number of confirmed cases in Wuhan could also be due to several other factors. These include a time lag between infection and symptom onset, delays in infected persons coming to medical attention and time taken to confirm cases by laboratory testing.
- Based on its estimates the research recommends to authorities worldwide preparedness plans and mitigation interventions should be readied for quick deployment. These include securing supplies of test reagents, drugs, personal protective equipment, hospital supplies and, above all, human resources.
- Given the lack of a robust and detailed timeline of records of suspected, probable and confirmed cases and close contacts, the true size of the epidemic and its pandemic potential remains unclear.


![Photo of [Nature Microbiology] Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/Image-2-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of [Cell Reports Medicine] Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in golden Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/fx1_lrg-e1601870075235-390x220.jpg)