Research
[The Lancet Microbe] Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: an observational study
The Lancet Microbe, 21 April 2020
Hin Chu, Jasper Fuk-Woo Chan, Terrence Tsz-Tai Yuen, Huiping Shuai, Shuofeng Yuan, Yixin Wang, Bingjie Hu, Cyril Chik-Yan Yip, Jessica Oi-Ling Tsang, Xiner Huang, Yue Chai, Dong Yang, Yuxin Hou, Kenn Ka-Heng Chik, Xi Zhang, Agnes Yim-Fong Fung, Hoi-Wah Tsoi, Jian-Piao Cai, Wan-Mui Chan, Jonathan Daniel Ip,Allen Wing-Ho Chu, Jie Zhou, David Christopher Lung, Kin-Hang Kok, Kelvin Kai-Wang To, Owen Tak-Yin Tsang, Kwok-Hung Chan, Prof Kwok-Yung Yuen
Highlights:
- Systematically investigated the cellular susceptibility, species tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage of SARS-CoV-2 and compared findings with those for SARS-CoV.
- Used one-way ANOVA to compare SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV replication in different cell lines and the cell damage each virus caused
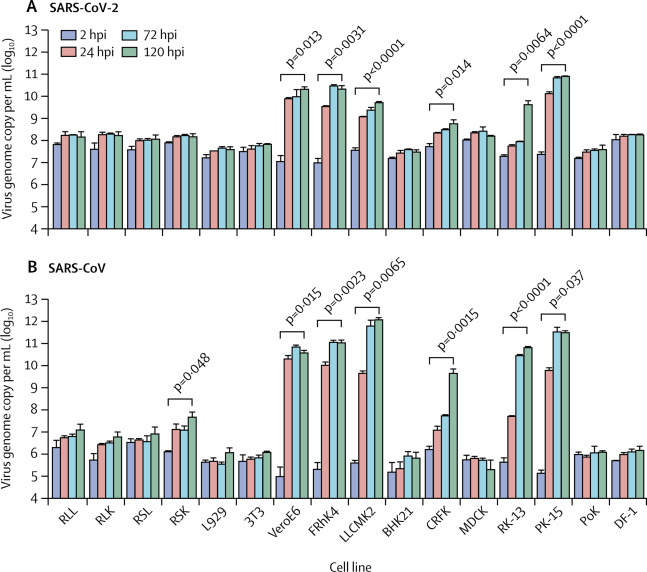
- SARS-CoV-2 infected and replicated to comparable levels in human Caco2 cells and Calu3 cells over a period of 120 h (p=0·52).
- By contrast, SARS-CoV infected and replicated more efficiently in Caco2 cells than in Calu3 cells under the same multiplicity of infection (p=0·0098).
- SARS-CoV-2, but not SARS-CoV, replicated modestly in U251 (neuronal) cells (p=0·036).
- For animal species cell tropism, both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replicated in non-human primate, cat, rabbit, and pig cells. SARS-CoV, but not SARS-CoV-2, infected and replicated in Rhinolophus sinicus bat kidney cells.

![Photo of [Nature Microbiology] Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/Image-2-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of [Cell Reports Medicine] Oral SARS-CoV-2 inoculation establishes subclinical respiratory infection with virus shedding in golden Syrian hamsters](https://fightcovid19.hku.hk/content/uploads/2020/10/fx1_lrg-e1601870075235-390x220.jpg)